Contents
- 1 Femur of a frog Introduction to Femur Bone in Frogs
- 2 I. Overview of the Frog Anatomy
- 3 II. Common Injuries and Ailments Affecting the Femur of a Frogs
- 4 III. Treatment Options for Femur Injuries and Ailments | Femur of a frog
- 5 IV. Care and Rehabilitation After Treatment|Femur of a frog
- 6 V. Conclusion of femur of a frog
Femur of a frog Introduction to Femur Bone in Frogs
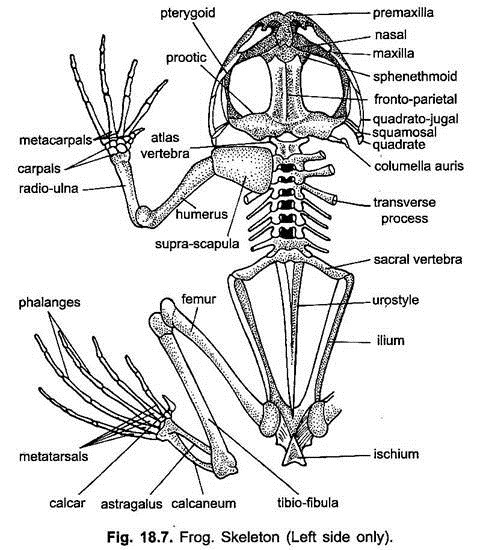
Femur of a frog : Frogs, with their unique anatomy and diverse adaptations, have captivated the human imagination for centuries. One essential component of their skeletal structure is the femur bone, which plays a vital role in their mobility and overall locomotion. In this blog post, we will explore the significance of the femur bone in frogs, common injuries and ailments that affect it, the available treatment options, and how to ensure optimal femur health for these fascinating amphibians.

I. Overview of the Frog Anatomy
To understand the femur bone’s function, it is crucial to have a basic understanding of frog anatomy. Frogs possess a streamlined body with four limbs, specialized for different purposes. The femur bone, commonly known as the thigh bone, is a long and sturdy bone that forms part of the hind limb structure in frogs.
II. Common Injuries and Ailments Affecting the Femur of a Frogs
A. Fractures: Causes, Symptoms, and Diagnosis femur of a frog
- Trauma-induced Fractures:
Frogs can experience femur fractures due to traumatic incidents such as falls, predator attacks, or accidental injuries. These fractures can cause severe pain and hinder the frog’s ability to move. Common symptoms include limb deformity, swelling, and reluctance to bear weight on the affected limb. Veterinarians diagnose femur fractures through physical examination and possibly with the aid of diagnostic imaging techniques like X-rays or CT scans.
- Stress Fractures from Overuse:
Just like humans, frogs can also experience stress fractures due to repetitive or excessive strain on their femur bones. Activities such as jumping, climbing, or excessive exercise can lead to microcracks developing in the bone, eventually resulting in stress fractures. Symptoms may include lameness, swelling, and tenderness around the fracture site. Diagnosis is typically performed through physical examination and imaging studies.
- Diagnosing Femur Fractures in Frogs:
Veterinarians specializing in exotic animal medicine utilize their expertise and diagnostic tools to identify and classify femur fractures in frogs accurately. They rely on clinical signs, radiographic images, and the knowledge of frog anatomy to determine the extent and severity of the fracture, which helps guide the appropriate treatment plan.
You are Reading Femur of a frog
Alarming Mutation of Avian Flu Raises Concerns for a New Global Pandemic 2024
B. Osteomyelitis: Infection in the Femur Bone |femur of a frog
- Causes and Risk Factors:
Osteomyelitis, a bacterial infection of the femur bone, is a serious condition that can affect frogs. Common causes of osteomyelitis include open wounds, untreated fractures, and systemic infections that spread to the bone. Frogs that have compromised immune systems due to stress, poor nutrition, or environmental factors are more susceptible to developing osteomyelitis.
- Symptoms and Diagnosis:
Frogs with osteomyelitis often present with localized swelling, pain upon limb manipulation, and in severe cases, systemic signs such as lethargy, anorexia, and fever. Diagnosing osteomyelitis involves a combination of physical examination, radiographic imaging, and laboratory tests, which may include blood work and the analysis of bone or joint aspirates.
- Treating Osteomyelitis in Frogs:
Successful treatment of osteomyelitis requires a multifaceted approach. It often involves a combination of antimicrobial therapy, surgical debridement of infected bone tissue, supportive care, and optimizing the frog’s environment to promote healing. Close collaboration between the veterinarian and the frog owner is crucial for monitoring progress and adjusting the treatment plan as necessary.
C. Bone Tumors: Recognizing and Addressing the Issue|femur of a frog
- Types of Bone Tumors in Frogs:
Bone tumors, although relatively rare in frogs, can occur and significantly affect their femur bones. Common types of bone tumors in frogs include osteosarcoma, chondrosarcoma, and fibrosarcoma. These tumors can arise spontaneously or due to genetic predisposition, environmental toxins, or viral infections.
- Signs and Symptoms of Bone Tumors:
Signs of bone tumors in frogs may include localized swelling, lameness, deformity, and reluctance to use the affected limb. As the tumor progresses, frogs may exhibit weight loss, loss of appetite, and lethargy. Veterinarians may utilize radiographs, ultrasounds, or biopsies to establish a definitive diagnosis.
- Treatment Options for Bone Tumors:
Treatment for bone tumors in frogs often involves a combination of surgical intervention, chemotherapy, and supportive care. Depending on the tumor’s type, location, and stage, veterinarians will determine the most appropriate treatment strategy. Close monitoring and follow-up are essential to evaluate treatment response and ensure the best possible outcome for these unique patients.
III. Treatment Options for Femur Injuries and Ailments | Femur of a frog
A. Conservative Management Approaches
- Rest and Immobilization:
For less severe femur fractures, conservative management may be appropriate. This involves restricting the frog’s activity and providing a supportive and safe environment that allows the bone to heal naturally. This approach often requires isolating the frog in a smaller enclosure and minimizing stressors.
- Pain Management Strategies:
Effective pain management is crucial for frogs recovering from femur injuries. Veterinarians may prescribe appropriate analgesics to alleviate discomfort and enhance the frog’s overall well-being during the healing process.
- Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation:
Physical therapy is a valuable component of femur injury recovery in frogs. This may include gentle exercises to maintain joint flexibility, range-of-motion movements, and gradual rehabilitation activities to rebuild muscle strength. Environmental enrichment, such as providing varied climbing surfaces or simulating natural hunting behaviors, can aid in the recovery process.
B. Surgical Interventions for Severe Cases
- Internal Fixation Techniques:
In complex femur fractures or cases involving bone tumors, surgical intervention may be necessary. Internal fixation techniques, such as the use of pins, screws, plates, or wires, provide stability and promote proper bone healing. The choice of technique depends on the specific fracture/tumor characteristics and the frog’s overall condition.
- External Fixation Methods:
External fixation methods, such as external skeletal fixators or external coaptation techniques, are alternative surgical approaches for treating femur fractures in frogs. These techniques stabilize the bone externally and allow for easy adjustment and monitoring during the healing process.
- Rehabilitation Post-Surgery:
Post-surgical rehabilitation is crucial for optimizing recovery and ensuring proper limb function. Physical therapy, wound care, and close monitoring of the surgical site are essential components of post-surgical management. Gradual reintroduction to normal activities and a supportive environment aid in the frog’s successful rehabilitation.
C. Preventive Measures to Promote Femur Health in Frogs | femur of a frog
- Maintaining Optimal Habitat Conditions:
Creating an appropriate habitat for frogs is essential for preventing femur injuries and ailments. This includes providing adequate moisture levels, appropriate temperature gradients, and suitable substrates that minimize the risk of falls or repetitive stress injuries.
- Appropriate Handling and Husbandry Techniques:
Practicing proper handling techniques when interacting with frogs minimizes the risk of accidental injuries. Additionally, maintaining good husbandry practices, such as providing a balanced diet, maintaining clean enclosures, and minimizing environmental stressors, promotes overall health and helps prevent femur-related issues.
- Regular Veterinary Check-ups and Care:
Regular veterinary check-ups are crucial for monitoring the overall health and detecting any potential femur issues early on. Experienced reptile and amphibian veterinarians can perform thorough physical examinations, provide preventive care, and offer advice on maintaining optimal femur health for pet frogs.
IV. Care and Rehabilitation After Treatment|Femur of a frog
A. Post-Treatment Monitoring and Evaluation
- Follow-up Veterinary Visits:
After receiving initial treatment, frogs with femur injuries or ailments require regular follow-up visits with their veterinarian. These visits allow for monitoring the healing process, assessing the frog’s response to treatment, and making any necessary adjustments to the care plan.
- X-rays and Diagnostic Tests:
X-rays and other diagnostic tests, such as CT scans or ultrasounds, are valuable tools for evaluating the healing progress of femur injuries or identifying any potential complications. Veterinarians may utilize these imaging techniques at specific intervals to ensure the bone is healing correctly.
- Assessing Healing Progress:
Monitoring the healing progress involves assessing factors such as pain levels, range of motion, and weight-bearing capacity. Veterinarians will provide guidance on when the frog can resume normal activities based on their evaluation of healing progress.
B. Physical Therapy and Exercises for Recovery |femur of a frog
- Passive Range of Motion Exercises:
Passive range of motion exercises can help maintain joint flexibility and prevent stiffness, especially during the healing process. Gently manipulating the affected limb through its natural range of motion promotes optimal healing and minimizes the risk of complications.
- Strengthening Exercises:
Gradual introduction of strengthening exercises helps rebuild muscle strength and promotes proper limb function. These exercises can include gentle resistance training or stimulating activities that encourage the frog to use the affected limb.
- Environmental Enrichment for Mobility Improvement:
Creating an enriched environment promotes mobility improvement and helps frogs adapt to physical changes due to injuries or surgeries. Providing climbing structures, natural hiding spots, or toys that encourage exploration can enhance the frog’s overall well-being and speed up the recovery process.
C. Adjustments in Diet and Environmental Factors for Long-term Health |femur of a frog
- Nutrition Guidelines for Femur Healing:
A proper diet is essential for the healing process in frogs. It is crucial to provide a well-balanced diet that meets the specific nutritional needs of the frog. Adequate calcium supplementation is especially important for maintaining bone health and supporting healing bone fractures.
- Adequate Space and Enclosure Design:
The size and design of the enclosure significantly impact a frog’s overall health, including femur health. Providing ample space for movement, appropriate hiding spots, and carefully selected substrates reduces the risk of falls, stress fractures, or other femur-related injuries.
- Behavioral Stimulation and Stress Reduction:
Enrichment activities, such as mimicking natural hunting behaviors or providing interactive feeders, help reduce stress and encourage normal behavioral patterns. A stress-free environment supports the frog’s healing process and overall well-being.
V. Conclusion of femur of a frog
Understanding the femur bone’s role and ensuring optimal femur health is essential for the overall well-being of frogs. Femur injuries, osteomyelitis, and bone tumors can significantly impact a frog’s mobility and quality of life. Treatment options vary depending on the severity and nature of the condition, ranging from conservative management to surgical interventions. Preventive measures, regular veterinary care, and post-treatment rehabilitation are crucial elements in promoting femur health in frogs. By implementing these strategies, we can help our amphibian friends leap back to health and continue fascinating us with their unique abilities.
Remember, your pet frog relies on you for its health and happiness. By taking the necessary steps to prevent femur injuries and providing appropriate care when needed, you play a vital role in ensuring a long and fulfilling life for your amphibian companion.
About femur of a frog
Please note that this blog post is for informational purposes only and should not be used as a substitute for professional veterinary advice. If you suspect your frog has a femur injury or any other health concern, consult with an experienced reptile and amphibian veterinarian for proper diagnosis and treatment.
External Sources :
- Scientific Journals and Research Papers:
- PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/
- Google Scholar: https://scholar.google.com/
- Veterinary Websites and Forums:
- Reptiles Magazine: https://www.reptilesmagazine.com/
- Reptile Forums UK: https://www.reptileforums.co.uk/
- Amphibian Conservation Organizations:
- Amphibian Survival Alliance: https://www.amphibians.org/
- International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN): https://www.iucn.org/
- Reputable Pet Care Websites:
- PetMD: https://www.petmd.com/
- American Society for the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals (ASPCA): https://www.aspca.org/
- Books and Academic Publications:
- “Amphibian Medicine and Captive Husbandry” by Kevin M. Wright (available on various online bookstores)
- “Amphibian Ecology and Conservation: A Handbook of Techniques” edited by C. Kenneth Dodd Jr. (available on various online bookstores)
Pertinent FAQs of femur of a frog:
- Can a frog survive a femur fracture without treatment?
- What are the common causes of bone tumors in frogs?
- How long does it take for a frog’s femur to heal after surgery?
- Are there any natural remedies that can help in femur recovery for frogs?
- Can physical therapy alone treat a femur fracture in frogs without surgery?
- How can I prevent femur injuries in my pet frog?

